An asteroid, named 1994 WR12, is racing towards Earth's orbit, and it is bigger than the Taj Mahal, said NASA. The number 1994 stands for the year it was discovered by US astronomer Carolyn S. Shoemaker at Palomar Observatory (November 28, 1994). It will pass by our planet today, Monday, about 3.8 million miles away.
The asteroid measuring 430ft, is massive and has the potential to initiate cataclysmic damage on whatever it crashes into, said the US space agency. Relatively, the size of this asteroid is double the size of the Big Ben clock in London. In another sense, measuring the same size and height as the Taj Mahal in India, at 240 feet high.

In a comparison of its destructive power, the asteroid has the potential of producing 77 megatons of TNT - if it crashes into any planet. The energy potential will be 1.5 times that of the biggest nuclear weapon ever tested, Tsar Bomba, which was exploded by Russia with 3,333 times that of the atom bomb dropped on Hiroshima in 1945.
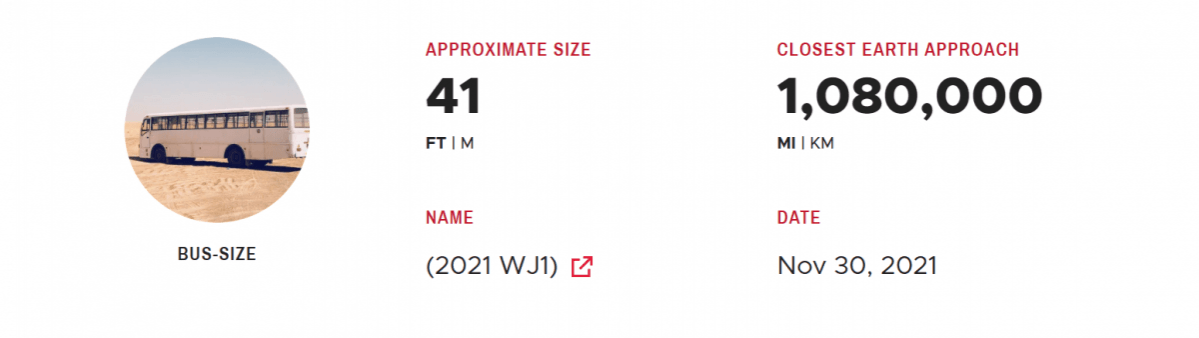
NASA's Asteroid Watch dashboard keeps tracking asteroids and comets which that will make relatively close approaches to Earth. Currently, it is showing five such major asteroids under watch.
The dashboard displays the date of closest approach, approximate object diameter, relative size and distance from Earth for each encounter. The object's name is displayed by hovering over its encounter date. Clicking on the encounter date will display a Web page with details about that object.
5 Major Asteroids Approaching Earth Soon
The NASA dashboard displays the next five Earth approaches to within 4.6 million miles (7.5 million kilometers or 19.5 times the distance to the moon); an object larger than about 150 meters that can approach the Earth to within this distance is termed a potentially hazardous object.



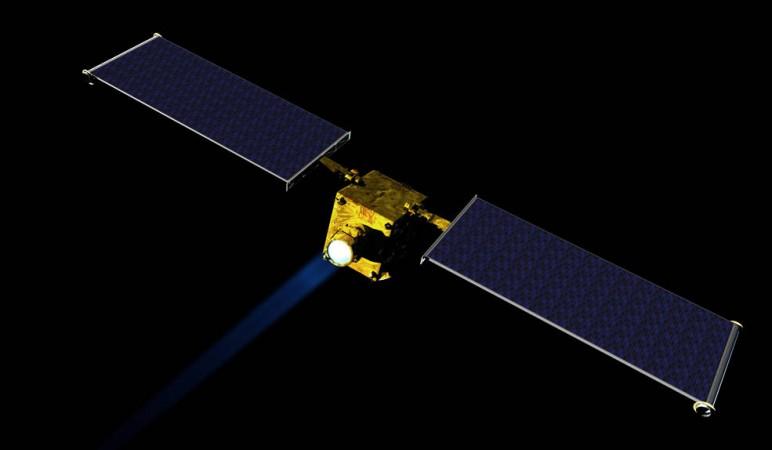
NASA's asteroid defence mission DART
The US space agency had launched the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) spacecraft, intended to deliberately crash into an asteroid on November 24 as a test of technology to see if it can change the motion of an asteroid in space.
The spacecraft target is the binary near-Earth asteroid Didymos and its moonlet, which pose no threat to Earth. "DART will be humanity's first test for planetary defence -- to see if we could change the course of an asteroid should we ever discover one headed toward Earth," said Thomas Zurbuchen, NASA's associate administrator for the science mission directorate, in a blogpost.

DART is scheduled to reach the Didymos binary asteroid system between September 26 and October 1, 2022. When it reaches Didymos, it will need to differentiate between its impact target Dimorphos and the larger parent asteroid that Dimorphos orbits, Didymos - all the while millions of miles away from Earth, Zurbuchen said.
While "Didymos system is not a threat to Earth... we need to be prepared should we ever be threatened by one of these enormous bodies emerging from the void of space," Zurbuchen said. The average distance between Earth and the moon is about 239,000 miles (385,000 kilometers).

















