
Whistleblower organisation WikiLeaks, which has been regularly exposing files from Central Intelligence Agency's (CIA) hacking toolkit for the last couple of months, has made one more file public and it is called Athena malware. It is a surveillance tool believed to have been created to get communications from Microsoft's operating system like Windows 10, Windows XP Pro and others.
Athena malware is a beacon loader developed with the US cybersecurity firm Siege Technologies designed to be injected into the target machine, according to the document of WikiLeaks' series of Vault 7 leaks. It is a surveillance tool, a simple implant application to capture files from Windows machines.
Also read: Forget WannaCry ransomware, these 3 new malware could bring scarier cyber nightmare
"Athena is the primary implementation for use on WinXP through Win10 operating systems. This implementation uses the RemoteAccess service for persistence, ZLIB for compression and XTEA for encryption on disk," according to the WikiLeaks' Vault 7 document.
Several Windows operating systems are vulnerable to the Athena malware.
"The target computer operating systems are Windows XP Pro SP3 32-bit (Athena only), Windows 7 32-bit/64-bit, Windows 8.1 32-bit/64-bit, Windows 2008 Enterprise Server, Windows 2012 Server, and Windows 10. Ubuntu v14.04 is the validated Linux version. Apache 2.4 is the validated web server for the Listening Post," said WikiLeaks document.
There is another implementation of the malware for Windows 8 through Windows 10 called Hera. It "uses the Dnscache service for persistence, BZIP2 for compression and AES 256 for encryption on disk.4.2.1 ((S//NF) On-Target Footprint(S//NF)."
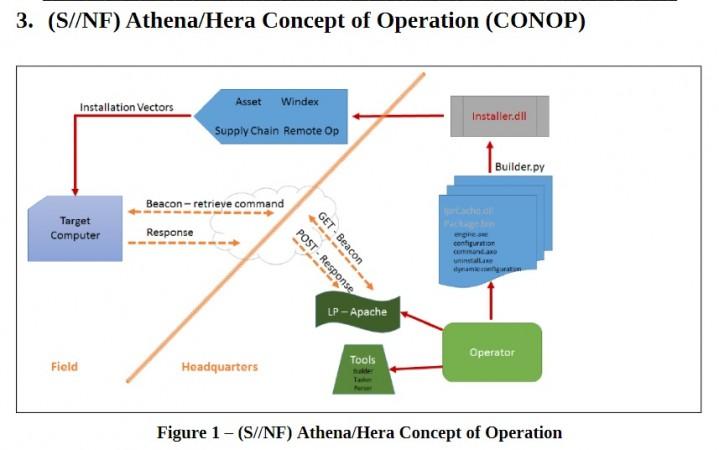
The whistleblower organisation said that Athena malware will provide a beaconing capability, the memory loading/unloading of malicious payloads for specific tasks and the delivery and retrieval of files to/from a specified directory on the target system once it is installed. The malware also allows the operator to configure settings during runtime to customize it to an operation.

















