As per the new 2022 list of Essential Drugs, antacid drug Ranitidine has been removed owing to the concerns that it has salt that could be carcinogenic or causes cancer.
Sold under brand names such as Aciloc, Zinetac and Rantac, salt in Ranitidine is has given room for concerns across the globe due to its cancer causing elements. It is a common drug prescribed by doctors to cure acid-related cough, indigestion, stomach pain and heartburn.
The element, known as N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) in Ranitidine medications, has become the subject of many studies that raised concerns about its probable human carcinogen feature though no concrete evidence has been established so far.
In 2020, the US Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) had withdrawn all prescription and over-the-counter (OTC) Ranitidine drugs from the market citing contamination by carcinogens. Even India's Central Drug Standards Control Organisation (CDSCO) has been reviewing the FDA decision in the country.
New List
A total of 384 drugs have been included in the National Lists of Essential Medicines (NLEM) 2022, which was released by the Union Health Minister Mansukh Mandaviya on Tuesday. The list has got the addition of 34 new drugs, while 26 from the previous list have been dropped.
The revision of NLEM 2022 has been done after constant consultation with stakeholders spanning from academia, industrialists and public policy experts etc., and crucial documents like WHO EML 2021.
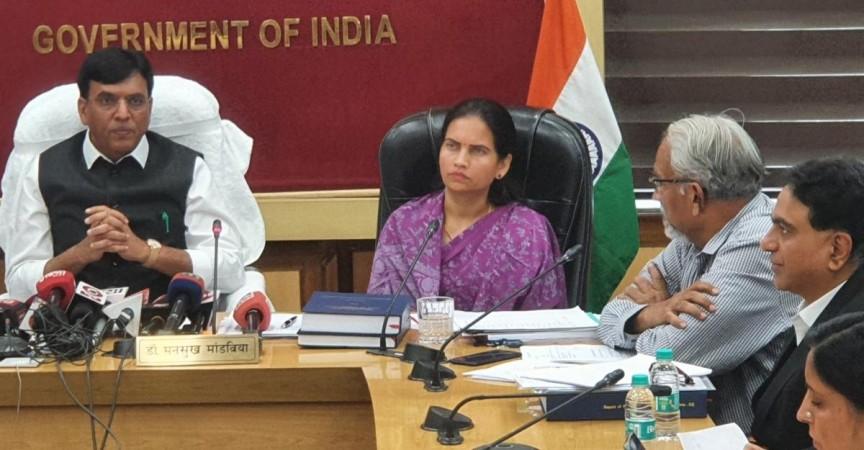

"This (NLEM) will give a boost to cost-effective, quality medicines and contribute towards reduction in out of pocket expenditure on healthcare for the citizens," said Mandaviya while launching the list.
In NLEM, the medicines are categorized based on level of healthcare system as: P- Primary; S- Secondary and T- Tertiary. The National List of Essential Medicines was first formulated in 1996 and it was revised thrice earlier in 2003, 2011 and 2015.
The drugs which are included in the list needs to be useful in diseases which is a public health problem in India, be licensed/approved Drugs Controller General (India) (DCGI) and have proven efficacy and safety profile.
When more than one medicine are available from the same therapeutic class, one prototype/medically best suited medicine of that class are included in the list. For the inclusion in the list, the price of total treatment is considered and not the unit price of a medicine.
Once the medicines are included in NLEM, manufacturers are required to sell their product equal to or lower than the ceiling price set by the government, thus reducing the profit margin but cannot stop its production as it is deemed important for national health and emergency scenarios.
A ceiling price calculation is based on the simple averaging of the market prices of different brands of medicines having a market share of at least 1%.