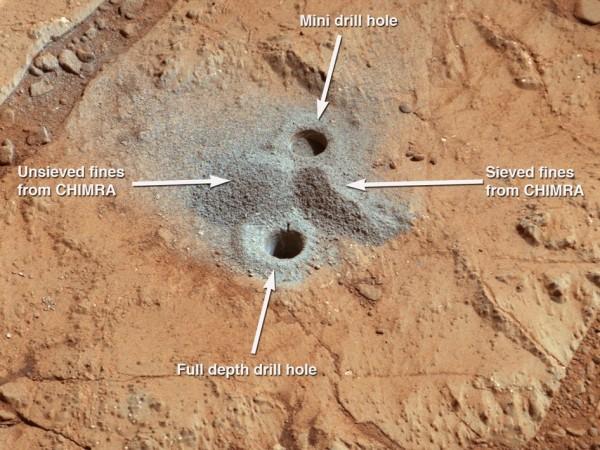
Nasa's Mars rover Curiosity has reported that the Red planet has lost a large part of its original atmosphere and is gradually turning cold.
The findings were based on the samples of selected gases collected by Curiosity showing significant changes in the planet's atmosphere over the years.
Sushil Atreya, co-investigator of Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) said, "We found arguably the clearest and most robust signature of atmospheric loss on Mars."
It was reported that gas was escaping from the surface, leading to its loss of almost 90 percent of the atmosphere.
Resarchers found that the planet's atmosphere contained "four times as much of a lighter stable isotope (argon-36) compared to a heavier one (argon-38)" which varies from what was previously recorded.
The obvious conclusion would point to the loss of lighter isotope over the heavier one. And the ratio of argon in the air is much lower than any other solar system like Sun and Jupiter.
Curiosity has also recorded a steep rise in the temperature of the planet over the last eight months when it was first recorded.
But fluctuating temperature could be a possibility of varying humidity in different parts of the planet.
According to the NASA, "Trails of dust devils have not been seen inside Gale Crater, but REMS sensors detected many whirlwind patterns during the first hundred Martian days of the mission, though not as many as detected in the same length of time by earlier missions."