Evolution has played a crucial role in determining the dominance of humans, and it is due to this phenomenon that modern-day human beings became intelligent, and smarter when compared to their ancestors. And now, a new scientific study has suggested that human beings continue to evolve in three specific areas.
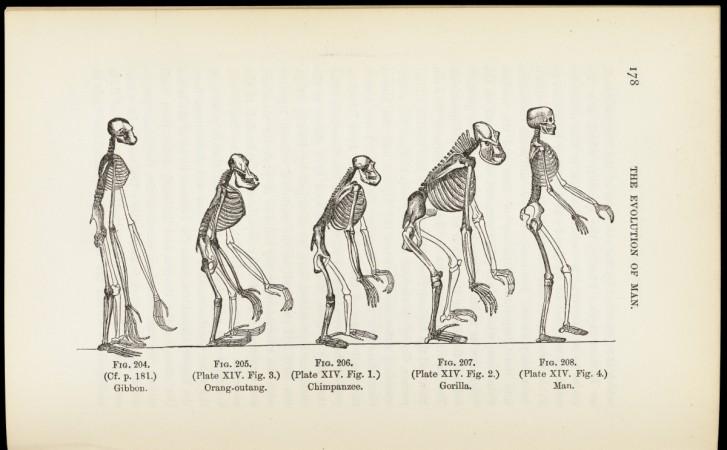
From ape-like species to advanced beings on earth
Human evolution can be considered as a long process that paved the way for advanced beings from ape-like ancestors. It was around four million years ago that humans developed the characteristics of bipedalism, the ability to walk on two legs.
It is through the process of evolution that human beings developed a large and complex brain when compared to other living beings on earth. The development of the human brain helped humans to develop their communication skills, both orally and written.
Three areas that are still evolving
According to Dr. Julie Parsonnet, a researcher at Stanford University, there are three areas where human beings continue to evolve, and one among them is reducing body temperature.
During the study, scientists noted that 98.6F was initially considered the ideal body temperature of humans, but in the last two decades, it is 97.9F, which means human beings have considerably reduced their body temperature, which is a part of evolution. Parsonnet noted that advancements and ease in the living atmosphere could have played a vital role in reducing the temperature of the human body.
Human genetic changes are another area that is undergoing evolution. According to the research team, human genes are developing lactose tolerance which is primarily due to the consumption of milk throughout life.
Despite all this milk consumption, the bones of human beings are becoming lighter and fragile, and this is the third area where evolution is happening. The strength of bones among modern humans is decreasing drastically due to the sedentary lifestyle, where physical activity is very less when compared to the old days. According to scientists, this transition began around 12,000 years back when humans switched from farming to hunting.

















