
The US space agency NASA continues to analyse the data from the accidentally discovered pulsars found around 50 years ago.
More than 2,000 pulsars were spotted by the astronomers by chance and despite being studied for five decades, much is not known about them.
NASA aims at digging out more about these collapsed stars with the help of its Neutron Star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) mission. The space agency aims to find out what the dense objects are really comprised of.
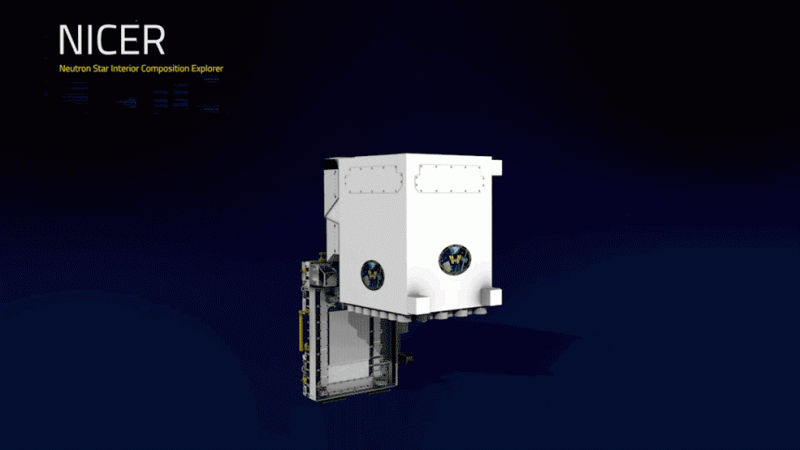
NICER was sent to the ISS in June on the SpaceX Dragon capsule. The first pulsar is dubbed PSR B1919+2.
"Many nuclear-physics models have been developed to explain how the make-up of neutron stars, based on available data and the constraints they provide," Keith Gendreau from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and the principal investigator for NICER, said in a statement Tuesday.
"NICER's sensitivity, X-ray energy resolution and time resolution will improve these by more precisely measuring their radii, to an order of magnitude improvement over the state of the art today," Gendreau added.
According to the popular hypothesis, pulsars and neutron stars are made of particles which scientists know about, like: protons, electrons, neutrons and quarks, but it's not known how exactly these particles react under extreme conditions.
"You can time the pulsations of pulsars distributed in many directions around a spacecraft to figure out where the vehicle is and navigate it anywhere," said Arzoumanian, who is also the NICER science lead. "That's exactly how the GPS system on Earth works, with precise clocks flown on satellites in orbit."
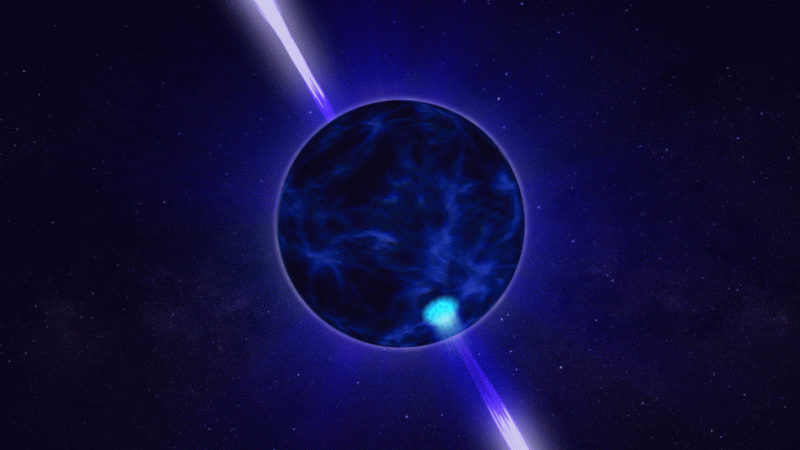
Here are 5 known things about pulsars:
- Pulsars refer to a white dwarf star or neutron star which emanates a beam of electromagnetic radiation.
- The objects have very short and regular rotational period, which make their radiation look more pulsating at regular breaks, similar to the light emitted from a lighthouse.
- The pulsars have seven to 20 times mass than Sun when they are still stars.
- Pulsars become turn smaller in size eventually. They can revolve up to hundreds of times per second.
- Despite being tiny, the pulsars are very dense and their solid surfaces have a temperature up to one million degrees.

















